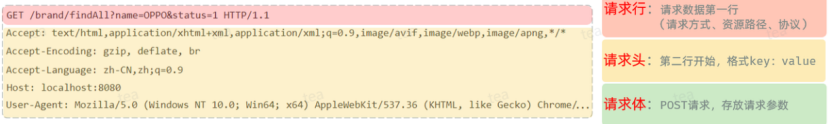
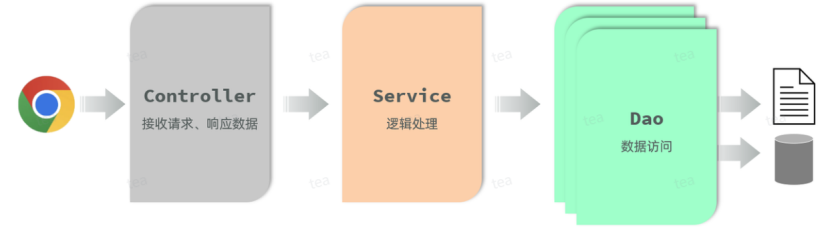
分层解耦
三层架构
- Controller:控制层。接收前端发送的请求,对请求进行处理,并响应数据。
- Service:业务逻辑层。处理具体的业务逻辑。
- Dao:数据访问层(Data Access Object),也称为持久层。负责数据访问操作,包括数据的增、删、改、查。
代码拆分
- 控制层:接收前端发送的请求,对请求进行处理,并响应数据
- 业务逻辑层:处理具体的业务逻辑
- 数据访问层:负责数据的访问操作,包含数据的增、删、改、查
分层解耦
内聚:软件中各个功能模块内部的功能联系。
高内聚:指的是一个模块中各个元素之间的联系的紧密程度,如果各个元素(语句、程序段)之间的联系程度越高,则内聚性越高,即 “高内聚”。
耦合:衡量软件中各个层/模块之间的依赖、关联的程度。
低耦合:指的是软件中各个层、模块之间的依赖关联程序越低越好。
解耦操作
- 控制反转: Inversion Of Control,简称IOC。对象的创建控制权由程序自身转移到外部(容器),这种思想称为控制反转。
对象的创建权由程序员主动创建转移到容器(由容器创建、管理对象)。这个容器称为:IOC容器或Spring容器。
- 依赖注入: Dependency Injection,简称DI。容器为应用程序提供运行时,所依赖的资源,称之为依赖注入。
程序运行时需要某个资源,此时容器就为其提供这个资源。
例:EmpController程序运行时需要EmpService对象,Spring容器就为其提供并注入EmpService对象。
- bean对象:IOC容器中创建、管理的对象,称之为:bean对象
IOC&DI入门
- 将Service及Dao层的实现类,交给IOC容器管理
在实现类加上 @Component 注解,就代表把当前类产生的对象交给IOC容器管理。
- 为Controller 及 Service注入运行时所依赖的对象
IOC
Bean的声明
IOC控制反转,就是将对象的控制权交给Spring的IOC容器,由IOC容器创建及管理对象。IOC容器创建的对象称为bean对象
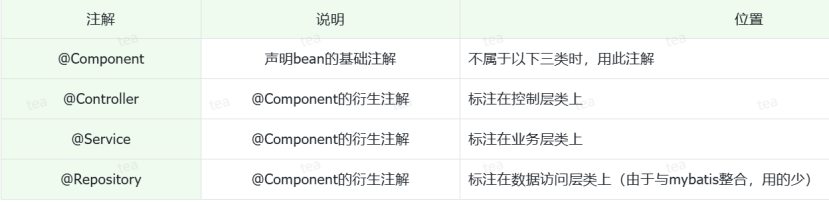
组件扫描
将项目中的所有的业务类,都放在启动类所在包的子包中,就无需考虑组件扫描问题。
DI
@Autowired用法
@Autowired 进行依赖注入,常见的方式,有如下三种:
- 属性注入:
优点:代码简洁、方便快速开发。
缺点:隐藏了类之间的依赖关系、可能会破坏类的封装性。
- 构造函数注入:
优点:能清晰地看到类的依赖关系、提高了代码的安全性。
缺点:代码繁琐、如果构造参数过多,可能会导致构造函数臃肿。
- setter注入:
优点:保持了类的封装性,依赖关系更清晰。
缺点:需要额外编写setter方法,增加了代码量。
@Autowired注解,默认是按照类型进行注入的
如果存在多个相同类型的bean,将会报错:
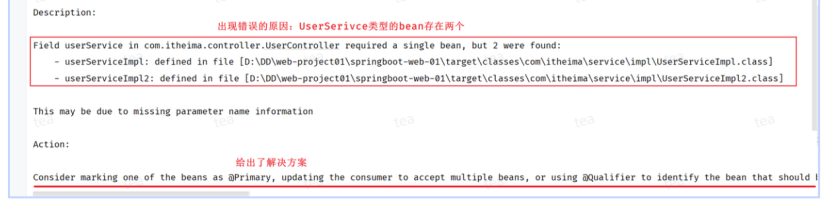
解决方法:
- 使用@Primary注解:
当存在多个相同类型的Bean注入时,加上@Primary注解,来确定默认的实现。
- 使用@Qualifier注解:
指定当前要注入的bean对象。 在@Qualifier的value属性中,指定注入的bean的名称。 @Qualifier注解不能单独使用,必须配合@Autowired使用。
- 使用@Resource注解:
是按照bean的名称进行注入。通过name属性指定要注入的bean的名称。
User.txt
1,daqiao,1234567890,大乔,22,2024-07-15 15:05:45
2,xiaoqiao,1234567890,小乔,18,2024-07-15 15:12:09
3,diaochan,1234567890,貂蝉,21,2024-07-15 15:07:16
4,lvbu,1234567890,吕布,28,2024-07-16 10:05:15
5,zhaoyun,1234567890,赵云,27,2024-07-16 11:03:28
6,zhangfei,1234567890,张飞,31,2024-07-16 11:03:28
7,guanyu,1234567890,关羽,34,2024-07-16 12:05:12
8,liubei,1234567890,刘备,37,2024-07-16 15:03:28
pojo
user.java
package org.example.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
//用户信息
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}
service.impl
UserService接口
package org.example.service;
import org.example.pojo.User;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserService {
// 查询所有用户信息
public List<User> findAll();
}
UserServiceImpl.java
package org.example.service.impl;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
import org.example.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl;
import org.example.pojo.User;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.List;
@Service
//@Component
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired //应用程序运行时,会自动的查询该类型的bean对象,并赋值给该成员变量
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public List<User> findAll() {
// 调用dao,获取数据
List<String> lines = userDao.findAll();
// 2.解析用户信息,封装成User对象 -> List<User>
List<User> userList = lines.stream().map(line -> {
String[] parts = line.split(",");
Integer id = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
String username = parts[1];
String password = parts[2];
String name = parts[3];
Integer age = Integer.parseInt(parts[4]);
LocalDateTime updatetime = LocalDateTime.parse(parts[5], DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
return new User(id, username, password, name, age, updatetime);
}).toList();
return userList;
}
}
UserServiceImpl2.java
package org.example.service.impl;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
import org.example.pojo.User;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.List;
//@Primary
@Service
//@Component
public class UserServiceImpl2 implements UserService {
@Autowired //应用程序运行时,会自动的查询该类型的bean对象,并赋值给该成员变量
private UserDao userDao;
@Override
public List<User> findAll() {
// 调用dao,获取数据
List<String> lines = userDao.findAll();
// 2.解析用户信息,封装成User对象 -> List<User>
List<User> userList = lines.stream().map(line -> {
String[] parts = line.split(",");
Integer id = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
String username = parts[1];
String password = parts[2];
String name = parts[3];
Integer age = Integer.parseInt(parts[4]);
LocalDateTime updatetime = LocalDateTime.parse(parts[5], DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
return new User(id +200, username, password, name, age, updatetime);
}).toList();
return userList;
}
}
Dao.impl
Userdao接口
package org.example.dao;
import java.util.List;
public interface UserDao {
// 加载用户实现类
public List<String> findAll();
}
Usredao.java
package org.example.dao.impl;
import cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Repository
//@Component 将当前类交给ioc容器管理
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public List<String> findAll() {
// 1.加载并读取user.txt文件,获取用户数据
InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("user.txt");
ArrayList<String> lines = IoUtil.readLines(in, StandardCharsets.UTF_8, new ArrayList<>());
return lines;
}
}
Controller
UserController.java
package org.example.Controller;
import cn.hutool.core.io.IoUtil;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.example.pojo.User;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import org.example.service.impl.UserServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
@RestController
public class UserController { //@ResponseBody作用:将controller返回值直接作为响应体的数据直接响应;返回值是对象/集合->json串->响应
// 方法一:属性注入
// @Qualifier("userServiceImpl")
// @Autowired
// private UserService userService;
@Resource(name = "userServiceImpl2")
private UserService userService;
// 方法二:构造器注入
// private UserService userService;
// @Autowired 当当前类中只存在一个构造函数时,@Autowired可以省略
// public UserController(UserService userService) {
// this.userService = userService;
// }
// 方法三:setter注入
// private UserService userService;
// @Autowired
// public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
// this.userService = userService;
// }
@RequestMapping("/list")
public List<User> list() throws Exception{
//// 1.加载并读取user.txt文件,获取用户数据
// InputStream in = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("user.txt");
// ArrayList<String> lines = IoUtil.readLines(in, StandardCharsets.UTF_8, new ArrayList<>());
//
//// 2.解析用户信息,封装成User对象 -> List<User>
// List<User> userList = lines.stream().map(line -> {
// String[] parts = line.split(",");
// Integer id = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
// String username = parts[1];
// String password = parts[2];
// String name = parts[3];
// Integer age = Integer.parseInt(parts[4]);
// LocalDateTime updatetime = LocalDateTime.parse(parts[5], DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
// return new User(id, username, password, name, age, updatetime);
// }).toList();
List<User> userList = userService.findAll();
// 3.返回数据(json)
return userList;
}
}